DBT vs Dataform
By Milan Philip | @intelia | October 23

Organisations have been using data warehouses as a central repository of data that allows firms to store and manage large amounts of structured and unstructured data from various sources. However, the data that comes into a data warehouse often needs to be transformed, cleaned, and modelled to make it operational for business analysis and reporting.
This is precisely where data transformation tools like DBT (Data Build Tool) and Google Dataform come into picture. These tools are designed to automate the process of transforming raw data into structured and useful information, which can then be analyzed and visualised by business analysts and data scientists.
Some familiar challenges that these data transformation tools solve include:

Both the tools are a great choice for managing and transforming data. But there are many differences that makes it worth exploring. Firstly, let us get to know both these tools better.
To start with, Google Dataform is a web-based data transformation tool which is designed to specifically work with BigQuery. It utilizes a custom scripting language called “Dataform Core” to define transformations and by doing so manage dependencies between them.
On the other hand, DBT is an open-source command-line tool that allows anyone to build and manage data transformation workflows in a modular and reusable approach. It utilizes SQL to communicate with data sources and is also designed to work with data warehouses like BigQuery, Snowflake, and Redshift. Additionally, DBT Cloud is a cloud-based platform that provides a managed and scalable solution for data transformation. It offers features such as a web-based UI, automated testing, scheduling, and monitoring of workflows. DBT Cloud also provides a collaborative environment for teams to work on data transformation projects. With DBT Cloud, users can focus on creating value from their data, rather than managing the infrastructure required to run the platform.
Now, let’s dive into the pros and cons of each tool
Google Dataform Pros:
1. Easy to use: Dataform makes it easy for analysts and data engineers to define and manage transformations because it has a user-friendly web-based interface.
2. Built for BigQuery: Dataform is specifically designed to work with BigQuery, which means that it can take advantage of some of the unique features and capabilities of that platform.
3. Automated dependency management: Dataform reduces the risk of errors and makes it easier to manage complex workflows because it automatically manages dependencies between transformations.
4. Scripting language: it is helpful for complex transformations because Dataform’s custom scripting language provides more flexibility and power than SQL.
Google Dataform Cons:
1. Proprietary: Unlike DBT, Google Dataform is a proprietary tool, which means that there is less community support and development.
2. Cost: Google Dataform offers its service for free, however, because Dataform runs queries in BigQuery, there are additional fees associated with running the queries which may be a barrier for some organizations. For instance, BigQuery cost $0.05 per GB of data processed after the free tier of 1TB data processed per month. Also, the use of a Google Cloud Platform project may incur additional charges from BigQuery usage or other services like Cloud Monitoring, Secret Manager and IAM.
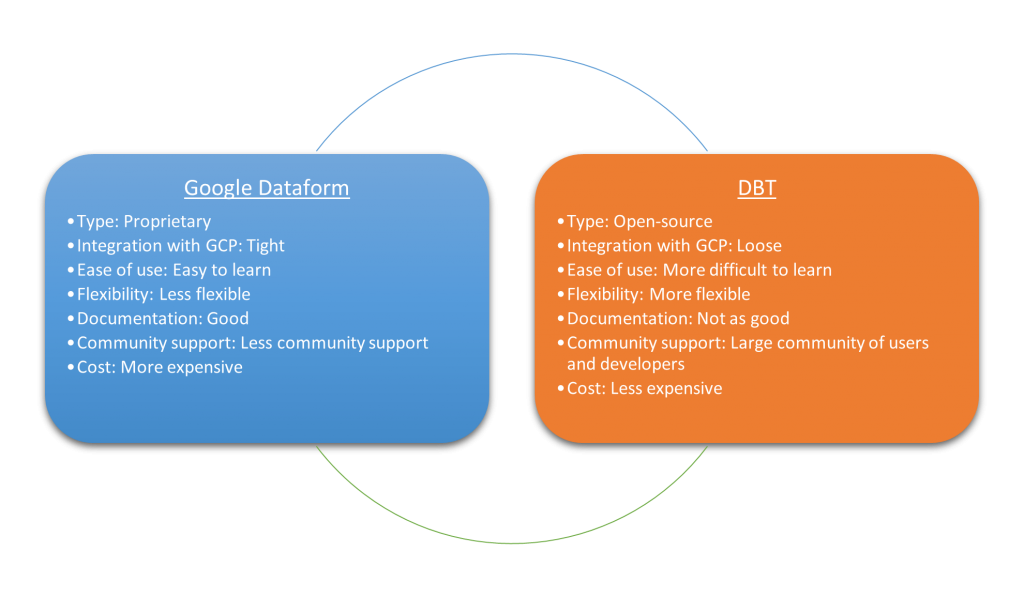
DBT Pros:
1. Modularity: DBT’s modular approach to building transformation workflows makes it easy to break down complex transformations into smaller, more manageable pieces.
2. Reusability: It saves time and reduces the risk of errors because DBT transformations are modular, they can be reused across multiple projects and datasets.
3. Open-source: DBT is an open-source tool, which highlights that it has a large and active community of users who contribute to its development and provide support.
4. SQL-based: Easy for analysts and data engineers to work with data and leverage their existing SQL skills because DBT’s uses SQL.
DBT Cons:
1. Limited to data warehouses: DBT is designed to work with data warehouses like BigQuery, Snowflake, and Redshift, which means that it may not be the best choice for organizations that use other types of data storage.
2. Command-line interface: While DBT has a web-based UI, it still requires a lot of work to be done through the command-line interface, which may not be ideal for some users.
3. Steep learning curve: DBT can be difficult to learn and requires a good understanding of SQL and data modeling concepts.
Conclusion
To sum up both DBT and Google Dataform are powerful tools for managing and transforming data. If you are using the Google Cloud Platform and BigQuery for your data warehousing needs, then Google Dataform is a powerful data transformation tool that can provide an integrated and seamless solution. Its custom scripting language and easy integration with BigQuery make it a standout winner in this environment. Furthermore, using Google Dataform may eliminate the need for additional tooling and integration efforts, saving you time and resources.
However, if you are using a different data warehouse, such as AWS or Snowflake, then DBT is the obvious choice due to its compatibility with multiple data warehouses and open-source flexibility. DBT’s modular and reusable approach to data transformation workflows allows for more efficient and scalable transformation pipelines. Additionally, DBT Cloud provides a managed and scalable solution for data transformation.
Ultimately, the choice between these two tools will depend on your specific requirements, including your data environment, team size, budget, and scalability needs.